MCT oil and coconut oil are both sourced from coconuts. But they’re not one and the same. Here’s what each oil is about to help you decide which oil is better for you.
Two oils that have become increasingly popular over the past couple of years are MCT oil and coconut oil. What’s interesting is that both are derived from the same ingredient and are often mentioned within the same contexts.
With these similarities, keto dieters and other health enthusiasts are left wondering if there are any differences between MCT oil and coconut oil. Some even ask, “Is MCT oil the same as coconut oil?”
Coconut oil and MCT oil may seem like the same thing, but they do have different compositions, uses, and benefits. Knowing more about each will help you decide which one is best for your diet.
Want to learn more about the difference between mct oil vs coconut oil? Let’s first explain what each one is.
MCT Oil
To understand what MCT oil is, you first want to know what MCT stands for.
The acronym MCT stands for medium-chain triglyceride. Triglycerides are types of lipids with a glycerol backbone and three fatty acid chains. These chains are of a medium length, which means comprising 6 to 10 (and some say 12) carbon atoms 1.
But chemistry aside, the most important thing to know is that the majority of the fats in our diets have long chains of fatty acids (LCTs) rather than medium ones.
Fats that fall under this category are those found in soy, corn, sunflower, and safflower oil 2. Other sources include butter, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
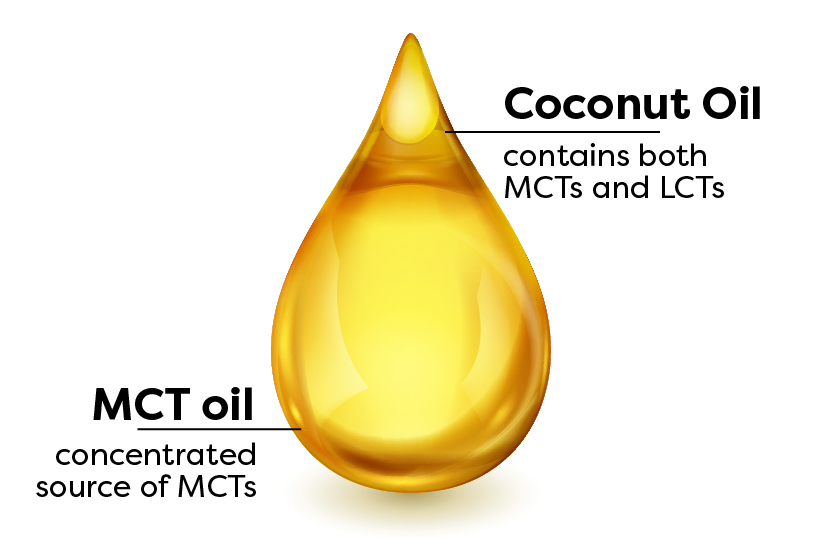
MCTs, on the other hand, are rare. There are only two major sources of them: coconut and palm kernel oil, and both, but usually coconut oil, are used to make MCT oil.
Staci Gulbin, MS, MEd, RD, LDN explains that
MCT oil is a concentrated source of MCTs, while coconut oil contains both MCTs and LCTs.”
Furthermore, MCT oil can be natural or synthetic 3. The latter involves steps like hydrolyzation from coconuts, purification, and re-esterification. The first involves simple distillation of virgin coconut oil.
Did you also know that MCTs boost brain health? Once ingested, they get converted into ketones which cross the blood-brain barrier.
The type of fat in MCT oil may improve brain function, specifically from a cognitive perspective,”
says Lisa Richards, CNC. One of the things that MCT helps with is your mental clarity.
Another thing to note about MCT oil is that there are several types:
- C8 Oil – This type is 100% caprylic acid, the most potent MCT there is. It’s called C8 because C stands for carbon and 8 for the number of carbon atoms in the fatty acid chain.
- C10 Oil – A fatty acid with a carbon chain of 10 atoms is also known as capric acid. Both C8 and C10 make up a small fraction of coconut oil, around 15 % 4.
- C8 & C10 Oil – You will also find MCT oil that contains both types of MCTs. This one is usually more affordable and gives you the best of both worlds.
Coconut Oil
A colorless to brown-yellow oil made from mature coconuts, coconut oil comes in two types: refined and virgin.
Refined coconut oil is made by extracting the oil from copra, which is the dried kernel of a mature coconut. The oil is then refined, bleached, and deodorized. Virgin coconut oil, on the other hand, is made via a wet process 5. This entails extracting the oil from coconut milk or fresh kernels.
The fatty acid composition of both types is the same. Both oils are 99.9% fatty acids, of which 92% are the saturated kind 5. This surpasses the saturated fat even of butter. However, the saturated fats in coconut oil are very different from that of butter – they’re mainly MCTs.
To explain it further: almost 50% of coconut oil is lauric acid (C12) and 15% is capric and caprylic acid 4. The rest is a mixture of LCTs such as palmitic acid, linoleic acid, and others.
Researchers say that lauric acid behaves both like an MCT and an LCT 6, 7. They also say it has distinctive properties not shared with longer-chain saturated fats, some of which include antimicrobial and cancer-fighting 8, 9.
MCT Oil vs Coconut Oil
Looking at a side-by-side comparison of MCT oil vs coconut oil can help you make your pick. Keep in mind that both oils come with their unique benefits and each one has different uses. Below are the most important things to consider when deciding.
Uses
MCT oil is used in the clinical setting or as a dietary supplement.
Doctors sometimes prescribe it to patients with fat metabolism disorders, gastrointestinal disorders, malnutrition, and malabsorption. The reason being that MCTs don’t require much work from the digestive tract – no bile, pancreatic enzymes, or proteins involved. Instead, they passively go to the liver from the small intestine via the portal vein 3.
As a dietary supplement, they’re especially popular among keto-ers. That’s because studies show that MCTs are highly ketogenic, meaning they promote ketone production 10. What’s more, they oxidize fairly easily and have slightly fewer calories than other types of fats (8kcal/gram vs. 9 kcal/gram). This means MCTs can promote weight loss if you take them in moderation in order to replace other fats in your diet 11.
You should never cook with MCT oil as it has a low smoke point.
Erik Abramowitz, NTP explains that
MCT oil is best with smoothies or in coffee,”
You can also use it in salad dressings, avocado dips, or add it to soup after it’s cooked.
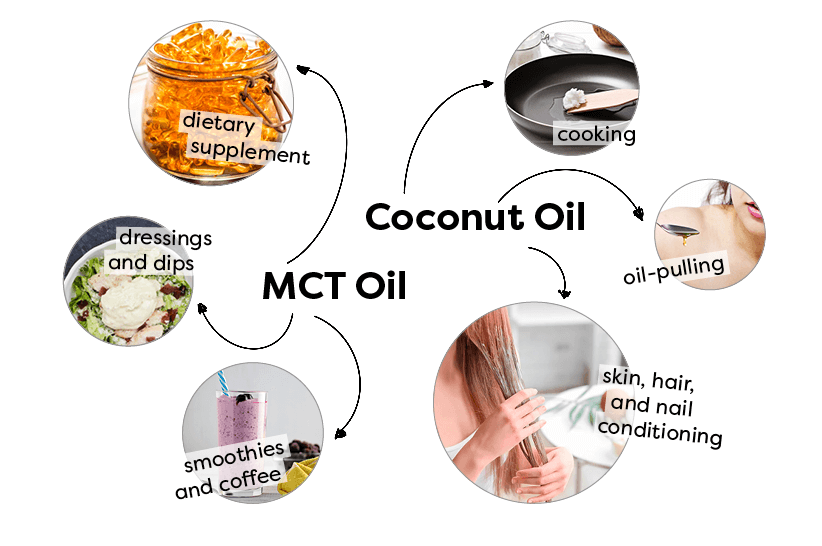
Coconut oil, on the other hand, is more than suitable in cooking with a smoke point at over 230°C. Virgin coconut oil has a distinct coconut-y taste, while its refined version is virtually flavorless. With that in mind, it’s best to use virgin coconut oil where you want to add coconut flavor and the refined version where a recipe calls for a neutral oil. Another popular use of virgin coconut oil is as a skin, hair, and nail conditioning ingredient and for oil-pulling.
Health benefits
MCT oil health benefits are wide and varied. But one of the most sought-after MCT oil benefits is definitely weight loss. As already explained, MCTs have fewer calories than other fats and they tend to oxidize (not get stored) fairly easily. If you replace some of the lower quality fats in your diet with MCTs, they might help you lose weight.
Furthermore, a study with 31 men and women compared MCT oil to olive oil for weight loss 12. The study found that MCT oil does not worsen metabolic syndrome. In fact, it seems to help reverse it.
Besides weight loss, MCTs can work as a source of energy on your keto diet. They’re practically a substitute for glucose and carbs for keto eaters.
Researchers have been looking into MCTs as an alternative source of energy for brains affected with Alzheimer’s Disease 13, and the results seem promising. Based on those findings, it’s fair to assume that MCT oil can have a favorable effect on healthy brains as well.
Coconut oil benefits come mainly from lauric acid and antioxidant compounds in the case of virgin coconut oil. Studies show that lauric acid has strong antimicrobial properties 14, which is why it’s used in oil-pulling. Applied to the skin and hair, coconut oil provides some UV protection and it can help prevent and treat atopic dermatitis.
Coconut oil also has a better effect on LDL cholesterol compared to butter but not as much as olive oil 14. When it comes to weight loss, however, there’s not much solid evidence since most studies on this subject were done on animals or used MCTs rather than coconut oil.
Risks and Considerations
Like all fats, coconut oil and MCT oil are relatively high in calories compared to carbs and protein. That’s why you need to consume them in moderation (1-4 tbsp daily) to get their weight-loss and other benefits; otherwise, you will gain weight with excessive intake. In other words, moderation is key if your goal with these oils (especially MCT oil) is weight loss.
Another thing to keep in mind is that neither is a significant source of essential fatty acids (omega 3 and 6). You will need to get these from other foods like fish, flaxseed, avocados, and walnuts; otherwise, you run the risk of deficiencies.
Furthermore, taking too much MCT oil can and often will lead to stomach pain, diarrhea, and vomiting 3. The tolerable MCT oil dosage is around 4-10 tablespoons or 50-100 grams daily, equally divided across meals. However, it’s best to start at 1 tablespoon and increase your daily dose gradually to build tolerance.
Daily intake of coconut oil can upset your stomach as well according to studies 15.
Staci Gulbin, MS, MEd, RD, LDN warns that,
Those with fat malabsorption issues, heart health issues, or with liver or pancreas conditions should not consume too much of these oils since they are very high in saturated fats and could place stress on the body during digestion.”
Verdict
MCT oil is better for weight loss and energy since it is a concentrated source of unique fats (C8 and C10) that boost ketone production, provides cells with immediate energy, and that resist being stored in fat cells. Coconut oil, on the other hand, is better as cooking oil, for fighting infections, and as a conditioning ingredient. It is mostly composed of lauric acid (C12), a saturated fat that can provide energy as well as contribute to weight gain.
So, at the end of the day, both oils have something to offer, which means that neither one is better than the other looking at the wider picture.
Takeaways
- MCT oil and coconut oil are derived from the same ingredients, but they’re completely different products.
- MCT oil is usually consumed as a dietary supplement, while coconut oil is a fantastic cooking oil with a high smoke point.
- Coconut oil comes with its own set of health benefits, but whether or not it’s good for weight loss is under debate.
- Combining them on your diet can help you get the best of both worlds since both have their own set of uses and benefits.










![Juicing for Weight Loss: Everything You Need to Know [Plus Recipes]](/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/Juicing-for-Weight-featured-image.jpg)