The keto diet and diabetes are two interesting areas of discussion. Because if you have or are at risk for diabetes, you’re probably wondering whether a low-carb and high-fat diet helps.
People diagnosed with diabetes struggle with high blood sugar levels. Diabetes happens when the body cannot create or utilize insulin – a hormone that allows sugar to enter the cells. This causes glucose to build up in the bloodstream 1.
Since the keto diet limits carbohydrates, one could ask, “Is a keto diet safe for diabetics?”
Knowing that carbs turn into glucose, the idea of reducing blood sugar through a low-carb diet makes sense.
But let’s not jump into conclusions yet.
In this article, we’re going to explore the connection between keto and diabetes. Can diabetics do keto? What do studies say?
Is the Keto Diet Safe for You if You Have Diabetes?
That depends on the type of diabetes you have.
There are 3 major types of diabetes, which are – Type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes.
A brief recall about each type:
In type 1 diabetes, the body cannot produce insulin. This means that a person has to depend on insulin daily to function normally.
Meanwhile, in type 2 diabetes, the body still produces insulin. However, the cells don’t respond effectively to it. This phenomenon is known as insulin resistance.
Finally, there’s gestational diabetes which can only happen during pregnancy.
To dive deeper into the question, is keto safe for diabetics? We need to consider the studies that have been conducted so far.
Here’s what we know:
Research tells us that a low-carb, ketogenic diet improves blood glucose control in those with type 2 diabetes.
In a 2005 study, participants were instructed to limit their carbs to 20 grams or less per day initially. There were no restrictions on dietary fat. However, trans fats were minimized 2.
The result? Their fasting blood glucose and hemoglobin A1c improved. And because of that, their diabetes medications were reduced 2.
Another study, conducted by Virta Health, showed how effective nutritional ketosis can be in resolving type 2 diabetes. The participants started with 30 grams of carbs or less per day, and this was gradually increased based on their tolerance 3.
Results showed an improvement in their HbA1c, fasting glucose, fasting insulin, weight, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels 3.
These studies show that a person can conquer type 2 diabetes with a ketogenic diet when done correctly.
But what about type 1 diabetes and gestational diabetes?
More studies need to be done on them. In type 1 diabetes, higher ketone levels could lead to a dangerous condition called ketoacidosis 4.
And while it is possible for these conditions to limit carbs in their diet, they need close supervision from their doctor.
The Effect of Keto Diet on Your Blood Glucose
Ketogenic diets are very low in carbohydrates and high in fat.
Sugar consumption decrease has a good impact on a diabetic’s health and may highly improve one’s pancreas function.
This mostly concerns blood glucose level – reduction of sugary products helps to prevent the body from blood sugar spikes,” says Paulina Nowak, a registered dietician.
This carb reduction reduces a person’s need for insulin. That explains why those with type 2 diabetes can reduce or eliminate their medications (except for metformin).
Since the body is low on glucose, it needs another source of energy. In this case, fat produces ketones, which are a more efficient fuel than glucose 5.
What should blood sugar levels be in ketosis? The normal reading for blood glucose is 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) or lower.
Other Known Potential Benefits of the Keto Diet for Type 2 Diabetes
The keto diet and diabetes make a good match. Reducing carbs offer other health advantages on top of blood glucose control. These include:
Weight loss
A keto diet for diabetics can be a great way to lose weight. The American Diabetes Association stated that weight loss helps improve blood glucose levels 6.
When you deprive your body of carbs, glycogen is depleted. This forces your body to burn its stored fat 7.
Research shows that low-carb diets lead to greater weight loss than low-fat diets. A person on a keto diet can lose as much as 10 pounds in 2 weeks 7.
But take note that this initial weight loss is due to water weight, followed by fat loss 7.
Improvements in cholesterol
Many people with diabetes also struggle with high cholesterol levels. The condition lowers good cholesterol and increases bad cholesterol, increasing the risk of heart disease.
To remain in good health, diabetes patients also need to prevent and treat abnormal cholesterol levels 8. Fortunately, this is possible through a low-carb, keto diet.
One study on obese patients showed how a ketogenic diet effectively decreased total cholesterol levels while significantly increasing HDL and decreasing LDL. Triglycerides also lowered 9.
A person should also follow a ketogenic diet meal plan for diabetes that’s high in quality fats. These include monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) which you can get from olive oil, avocados, nuts 10.
Reduced dependence on medication
This is a huge benefit of the keto diet for type 2 diabetes. The diet’s glucose-lowering effect can reduce a patient’s need for medication.
Results from Virta Health’s 2-year clinical trial showed that diabetes medicines to control glucose were reduced. These included insulin and sulfonylureas 3.
Meanwhile, metformin was continued since it helped prevent type 2 diabetes from progressing 3.
Important: A keto diet may cause hypoglycemia in diabetes patients taking insulin. It should be carried out with a doctor’s guidance and supervision.
Lowered blood pressure
High blood glucose in diabetes damages the blood vessels. This explains why people who’ve had diabetes for a long time also have high blood pressure 11.
Is keto diet good for diabetics for lowering blood pressure (BP)? The answer is yes. It could be one of the most effective ways to normalize your BP naturally.
Dr. William S. Yancy, associate professor of medicine at Duke University Medical Center, says that a low-carb diet could be a better option for those with high blood pressure and weight issues 12. This is because a diet poses fewer side effects.
In his study, Dr. Yancy noted that nearly half of the patients decreased or stopped using blood pressure medications while following a low-carb diet. Their systolic BP dropped 12.
Increases insulin sensitivity
Recall that in type 2 diabetes, patients lose their sensitivity to insulin – something that a ketogenic diet can help with.
Being insulin-sensitive prevents a ton of health problems. These include obesity, high blood pressure, and even cancer 13.
Can the Keto Diet Reverse Type 2 Diabetes?
We already know the connection between nutritional ketosis and diabetes. But one question that keeps coming up is whether the diet reverses type 2 diabetes.
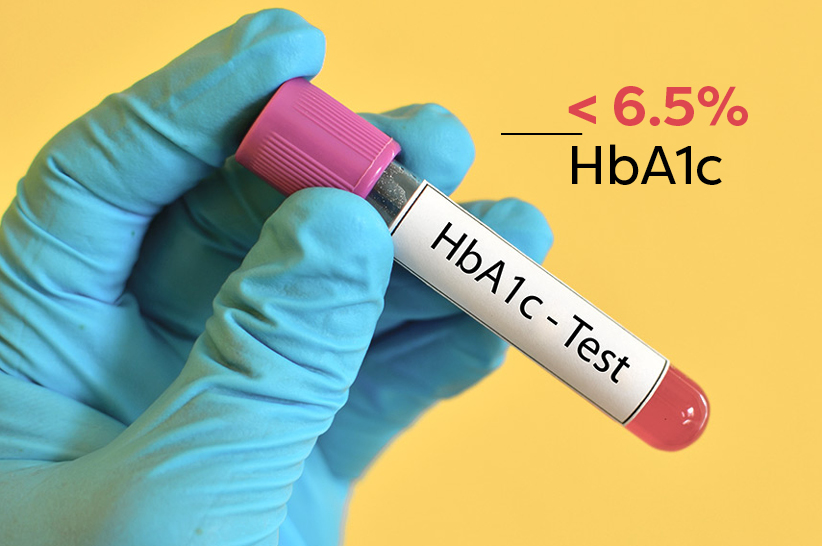
First of all, we need to define the term “reversal.” Here’s what it means:
A person achieves reversal when blood glucose stays normal without diabetes medications except for metformin. Specifically, HbA1c should remain below 6.5% 14.
Insulin sensitivity also increases while inflammation in the body lowers.
Carefully note that reversal does not imply cured. You only reverse type 2 diabetes for as long as you maintain your ketogenic lifestyle change. If not, symptoms of the disease return.
So yes, nutritional ketosis effectively reduces type 2 diabetes.
Potential Risks and Dangers
Following a keto diet causes you to experience some side effects. This is something we expect since the body has to adapt to its new fuel source.
A common short-term side effect is the keto flu. It’s a collection of flu-like symptoms such as weakness, headaches, diarrhea/constipation, and frequent urination. These can be resolved through electrolyte supplementation, hydration, rest, and eating more high-quality fats.
But here’s what you should know too:
If you don’t follow the diet properly, you could end up having health problems. This is why continuous medical supervision is important.
For example, overeating protein can cause high blood sugar on keto. Remember that protein should be kept to moderate levels.
Another mistake that could lead to an increased risk of heart disease is eating processed products that contain trans fats. “People who suffer from type 2 diabetes are by definition at higher risk of CVD (cardiovascular disease). That is why caution should be used,” says Nowak.
Most importantly – if you already have diabetes, you’d want to avoid hypoglycemia or worse, ketoacidosis.
Clinical supervision enables you to get the most out of the keto diet. This way, your doctor can adjust your medications and create an individualized plan that sustains ketosis.
We’ve covered the basic facts about diabetes and keto diet. Hopefully, this article helps you make smart decisions before getting started. Don’t forget to discuss with a medical practitioner first!
Takeaways
- The keto diet lowers blood glucose, which makes it a natural option for those with diabetes.
- More studies that show how nutritional ketosis helps with type 2 diabetes. Keto for type 1 diabetes and gestational diabetes requires further research.
- Other health aspects that the diet can improve include weight, blood pressure, medication use, insulin resistance, and cholesterol levels.










![Juicing for Weight Loss: Everything You Need to Know [Plus Recipes]](/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/Juicing-for-Weight-featured-image.jpg)








